Reading your electricity bill is not just a routine task; it is an essential step in understanding energy costs and consumption patterns. By familiarizing yourself with the components of your electricity bill, you can better grasp the structure of electricity charges, identify areas where you can save on electricity costs, and ultimately control energy usage. This awareness enables you to make informed decisions that can lead to lower electricity bills. Installing solar panels is an effective way to avoid rising electricity prices. By generating your own power, you can not only reduce your dependence on the power grid but also save on your monthly electricity costs.
What are the main components of an electricity bill? Your electricity bill may vary depending on the supplier, but most utility bills contain several common sections. Below is a breakdown of what each section represents:
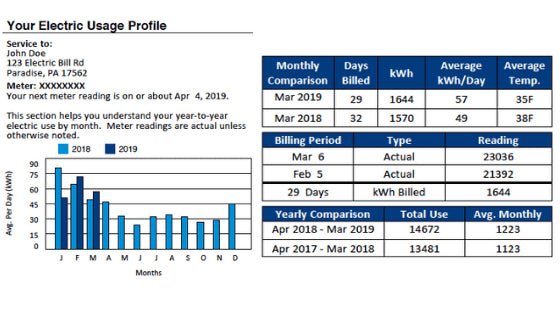
This allows you to identify trends or periods of unusually high usage. Your energy consumption will be broken down by type or time of use. If your utility provider offers Time-of-Use (TOU) rates, it will display your usage during peak and off-peak hours. Seasonal variations: Many consumers use more electricity in the summer (due to air conditioning) or winter (heating), which can be reflected in usage patterns.
By understanding when and how much electricity you use, you can find areas to reduce consumption, such as by reducing the use of high-energy devices during peak hours. Understanding rates and charges: Electricity costs are not fixed rates but vary based on various factors, including your rate plan and the time you use energy. Here are some things to note: Rate structures: Power suppliers typically use one of the following rate structures: Fixed rate: You pay a fixed price per kilowatt-hour for all the electricity you consume, regardless of when it is used. Tiered rate: The more electricity you use, the higher the price per kilowatt-hour. The first block of usage is cheaper, and with each subsequent block of increased usage, the price increases. Time-of-Use (TOU) rates: Electricity costs vary over time. Off-peak hours (such as late night and early morning) are cheaper, while peak hours (such as midday and evening) are more expensive. Demand charges (where applicable): Some utilities charge extra for high usage during peak demand periods. This is known as demand charges. It is based on the highest electricity cost you use during any 15-minute or 30-minute period within the billing cycle. If your bill includes demand charges, you will see them listed separately. These charges can be high, so reducing peak demand (for example, by spreading out the use of high-power appliances) can help lower your total bill. Taxes and adjustments: Electricity costs are not just about consumption. There are several additional charges to fund infrastructure, energy programs, and taxes. These include: Taxes and regulatory fees Sales tax: A percentage tax levied on the total bill. Environmental fees: Some states charge fees to fund renewable energy or energy efficiency projects. Adjustments: If your utility company made a mistake in the previous billing cycle, or if they need to correct undercharging or overcharging, you will see adjustments. These are one-time corrections that will appear as separate items on your bill. How to spot potential errors on your bill: Although power suppliers strive for accuracy, billing errors do occur. Here are some common errors to watch out for: Incorrect meter readings: If your bill includes estimated readings, they may not reflect your actual usage.Inaccurate readings may lead to overcharging. Unusual usage patterns: If your bill shows unusually high energy consumption, check for appliance malfunctions or changes in daily habits that could increase electricity usage. If discrepancies are found, you can contact your utility provider to dispute the charges or request a re-reading of your meter.
Solar system owners: How to read electricity bills after installation. If you have recently installed a solar system, you might wonder how to read your electricity bill now that you are generating your own power. The main change in your bill is net metering, which benefits many solar owners by providing credits for excess power generated and fed back into the grid. When your system is not generating electricity (e.g., at night), this credit offsets the electricity you consume from the grid. Look for the section on your bill that indicates net metering credits, which can significantly reduce your total bill. Reduction in current electricity usage: After installing solar panels, you will see a decrease in the ‘current electricity usage’ section of your bill. This reflects the energy you generate and use directly from your solar system. Changes in bill summaries: Your bill summary may include new categories that reflect solar usage. For example, you might see a line item for ‘Solar Generation,’ which shows how much electricity your solar panels produced during the billing period. Understanding charges: Even with solar power, your bill may still incur some costs, such as: connection fees, which cover the cost of grid access, and delivery fees, which still apply even if you produce your own energy because you use the grid as a backup power source. Rewards and rebates: If you are eligible for any state or federal incentives, such as tax credits or rebates, these may appear as items on your bill or be reflected in your overall savings. Advice for solar system owners: Track your production: Use applications or tools provided by your solar installer to monitor the energy generated by your system. This can help you determine if the system is operating as expected. Review your net metering statement: If applicable, carefully check your net metering statement to ensure that the credits match your solar production. Stay informed: Solar policies may change, so keep yourself updated on local regulations and utility practices regarding solar credits and billing. Utilize solar energy to reduce electricity bills: Don’t let electricity bills overwhelm you. Use solar energy today to start enjoying lower electricity costs and greater energy independence. At Hilden, we are committed to helping you transition smoothly and efficiently to solar energy.Our team specializes in providing high-quality solar systems tailored to your specific needs, ensuring that you minimize environmental impact while maximizing cost savings. Furthermore, we offer free consultations to discuss your options and identify the best solutions for you.